Floating solar mount structures for lake ,pond, and sea
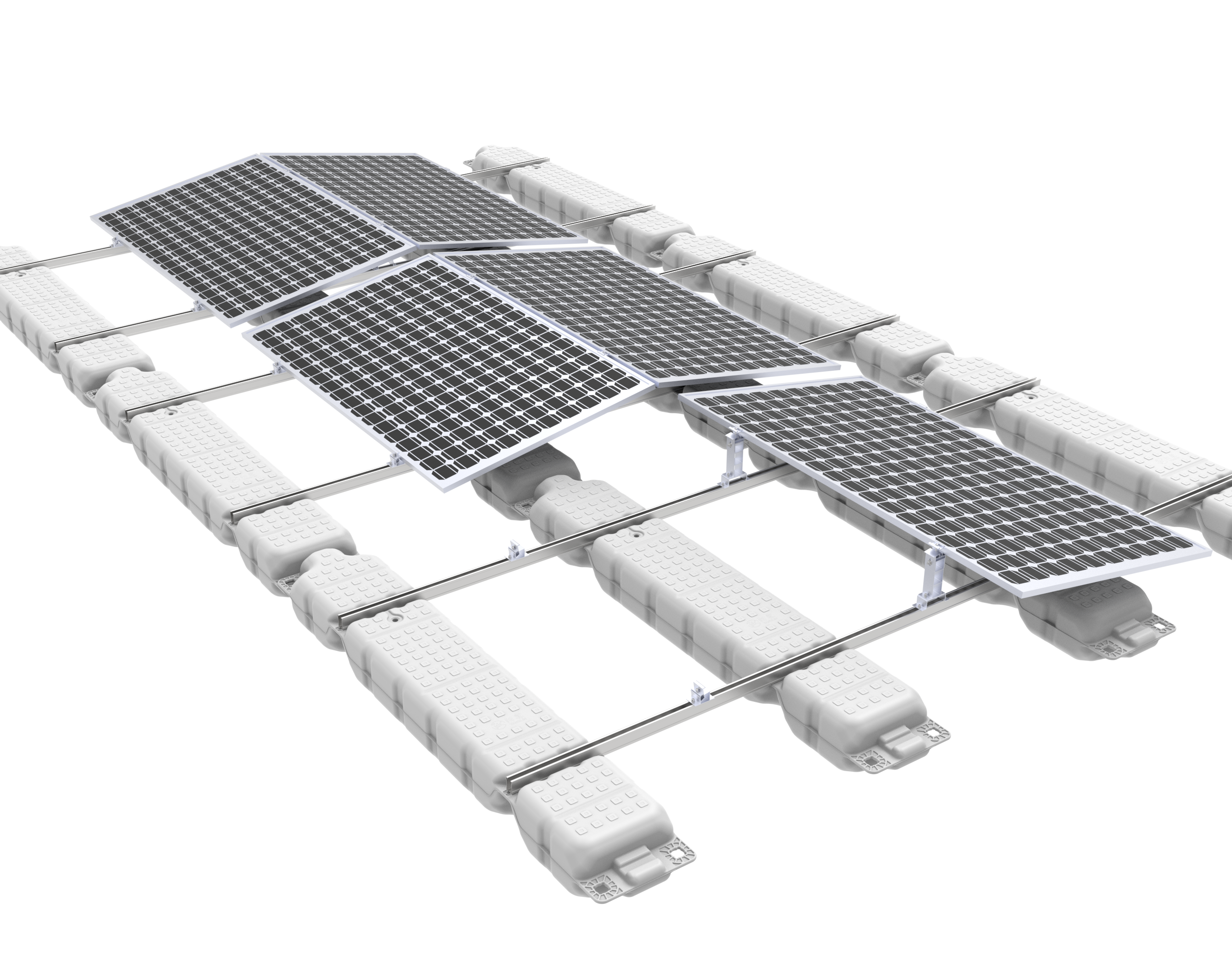
A floating PV (FPV) system is more complex than a ground mount, as it must be engineered for a harsh, corrosive, and dynamic environment.
Floating Structure
This is the foundation that provides buoyancy. The two primary designs are:
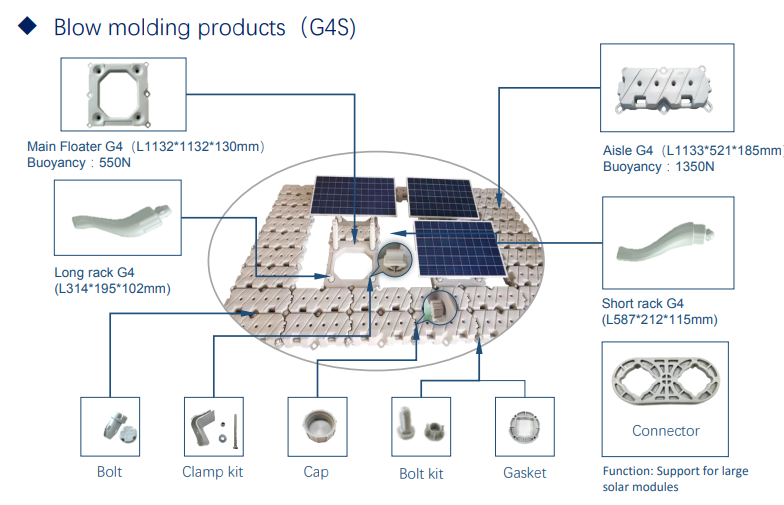
Modular Floats: Individual, often HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) floats are connected like a large raft. Each float holds one or a few panels. This is the most common design due to its modularity and ease of transport/installation.
Membrane-Based: A flexible, reinforced plastic membrane is stretched across a floating frame. The panels are mounted on top of this membrane. This design can cover large areas more continuously.
Mounting Structure:Similar to ground mounts, this is the frame that holds the panels at the correct angle. It is either integrated into the float or attached on top of it. Materials are typically aluminum or hot-dip galvanized steel for high corrosion resistance.
Mooring & Anchoring System: This is what keeps the entire array securely in place. It must withstand wind, waves, and changes in water level.
Anchors: These are placed on the bed of the waterbody. Types include deadweight anchors (concrete blocks), screw anchors (for softer beds), and drag-embedded anchors.
Mooring Lines: High-strength, UV-resistant ropes (e.g., nylon, polyester) or chains connect the floating structure to the anchors.
System Design: The mooring can be a spread mooring (multiple anchor points) or a tension-leg mooring (using buoyancy to keep lines taut), which is common in deeper waters.
Underwater Cable Management:Special submersible, rodent-proof DC cables connect the arrays. These cables are designed to withstand long-term UV exposure and immersion. They are held in place by cable trays or floating pontoons to prevent tangling and damage.
Floating solar mount structures represent a sophisticated and rapidly growing segment of the solar industry. By turning underutilized water surfaces into power generators, they offer a unique solution to land constraints while providing synergistic benefits like reduced water evaporation and enhanced panel efficiency.While the engineering, installation, and maintenance are more complex and costly than ground-mounted systems, the advantages in specific contexts—particularly on hydropower reservoirs, water treatment facilities, and in land-scarce regions—make floatovoltaics a crucial technology for the global energy transition. Its success hinges on careful environmental assessment, robust engineering for aquatic environments, and innovative mooring solutions.
Xiamen Starwin Solar is a manufacturer of solar mounting structures for over 13 years.
we' will need detail water area project information to design and quote exactly.
Any questions , please feel free to contact us ! Thanks
Xiamen Starwin Solar Technology Co.,Ltd
Add: No. 15 Donggang South Road, Huli District ,Xiamen City, Fujian Province , China
TEL:+86-592-2076007
FAX:+86-592-2076009
Email: sales6@starwinsolar.com
Cellphone:+8615280231187
whatsapp+8615206096360
website: www.starwinsolar.com